Model Used to Describe Enzyme Cycle
In this paper it is first shown why the E1E2 model must be discarded. Calvin Cycle requires the enzyme ribulose-15-bisphosphate carboxylaseoxygenase commonly called RuBisCO.

How An Enzyme Substrate Complex Works
Which model is sometimes used to describe enzyme-substrate interactions.

. Lock and key model. Describe what is happening in step 2 of the model. There are two models of the enzyme-substrate complex that scientists have proposed over the years.
This step is Strtoercoogenase IDH catalyzes the conversion c. 2 The enzyme grabs onto the substrate with a special area called the ACTIVE SITE. Although the use of static physical models has been shown to increase student understanding of a variety of topics including meiosis 10 and protein structure-function 11 the dynamic nature of enzyme-catalyzed reactions requires that the models depicting these reactions are also dynamic.
A model used to explain these results is that Mcm467 complexes are catalytic and the Mcm235 complexes are regulatory. But the common paradigm used to describe the reaction cycle of the P-type ATPases the E1E2 model is seriously flawed and this is hindering our progress toward this goal. The catalytic cycle of an enzyme action occurs in the following steps.
Describe what is happening in step 1 of the model. This model suggests that enzymes are flexible structures in which the binding of the substrate results in small changes to the shape of the active site maximizing its interaction. The location of the Krebs cycle enzymes in eukaryotes is in the _____ matrix while in prokaryotes the enzymes are found in the _____.
Ornithine serves as a carrier that is regenerated by the cycle. During step 3 of the Krebs cycle the enzyme isocitrate to a-ketoglutarate. NH 4 and aspartate provide the nitrogen that is used to produce urea and CO 2 provides the carbon.
But before we do that lets review the idea that enzymes make reactions go faster. Reactants that an enzyme act on are called. The substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme.
Carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized in the first reaction from NH4 CO2 and two ATP. The developed model can serve as a useful tool for predicting biogeochemical processes in natural environments either independently or through integration with hydrologic flow simulators. The answer to both questions lies in how enzymes interact with their substrates.
Microbial Metabolism flashcards containing study terms like in a metabolic pathway _____ and _____ multiple enzymes compete for a single substrate branches provide alternate methods for nutrient processing enzymes are bonded to one. The analogy he used was of a lock and key. Define the below terms and locate them on the model.
It generates the triose phosphates 3-phosphoglycerate 3-PGA glyceraldehyde-3P GAP and dihydroxyacetone phosphate DHAP all of which are used to synthesize the hexose phosphates fructose-16-bisphosphate and fructose 6-phosphate. Which model is sometimes used to describe enzyme-substrate interactions. And when you look at a reaction on a reaction coordinate diagram youd see that the catalyzed reaction would have a.
Todel 2 - Enzyme Cycle w Critical Thinking Questions 1. Are in the same area. This structure-based approach is complemented by thermodynamic models which provide abstract but quantitative descriptions of.
Enzymes are generally viewed as devices that use protein ar-chitecture to precisely position several key functional groups and electrostatic partners with respect to the substrate 14. Enzyme and reactant together is called. Inner mitochondrial plasma The electron transport chain is located in the __ membrane of eukaryotic cells and the __ membrane of bacteria.
This model states that the interaction between substrate and enzyme is weak and these weak interactions induce conformational changes rapidly and strengthen binding and bring catalytic sites close enough to substrate bonds. Antigen-antibody complex Lock-and-key Fluid mosaic. In 1890 the chemist Emil Fischer proposed that the substrate of an enzyme fits into the enzymes active site the physical location on an enzyme where the reaction takes place to form an enzyme-substrate complex.
However this model predicts a structure of dimers of trimers which is at odds with a planar structure found for the Archaeal helicase 76 96. The binding of the substrate induces a change in the shape of the enzyme molecule and the substrate firms itself more tightly into the active site. The tools they use should also be three-dimensional.
1 An enzyme and a SUBSTRATE. Reactions of the urea cycle. The Concerted model a and the Sequential model e are models used to explain the allosteric changes of conformation of an enzyme from the T structure to the R structure and viceversa.
The favourable model of enzyme-substrate interaction is called the induced-fit model. IDH is allosterically activated by ADP at high conco Describe how this interaction helps regulate the Krebs. Portion of enzyme that bind to reactants is called.
So today Im going to talk to you about the induced fit model of enzyme catalysis and how this concept can tell us a lot about how enzymes work. The substrate is the biological molecule that the enzyme will work on. Inorganic phosphate and two ADP are also produced.
There are four steps in the process of an enzyme working. The active site is a specially shaped area of the enzyme that fits around the. Start studying the Bio 150.
Memorize flashcards and build a practice test to quiz yourself before your exam. Induced Fit Model of Enzyme Action In 1958 scientist Daniel Koshland Jr PhD proposed the induced fit model to describe enzyme-substrate interaction. In the concerted model all the subunits that form the allosteric protein change conformation at once while in the sequential model the change in conformation of one subunit.

Enzyme Structure And Function Mini Project Structure And Function Student Reading Student Studying

During Photosynthesis The Enzyme Rubisco Does The Work Of Reducing Carbon Dioxide From The Atmosphere It Is Reac Photosynthesis Quotes For Book Lovers Enzymes

Defining An Enzyme Structure And Function Enzymes Biology Biochemistry Biology Diagrams

Mechanism Of Enzyme Action Enzymes Peptide Bond Active Site

Mechanism Of Enzyme Action Biochemical Chemical Bond Enzymes

How Digestive Enzymes Work And Why You Re Probably Deficient Digestive Enzymes Enzymes Biology Enzymes Activity

Introduction To Enzymes Active Sites Components Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Chemistry

Stop Gray Hair When It Starts With Catalase Xp No Gray Hairs Enzymes Biology Enzymes Blog Tips

Difference Between Brain Facts Science Biology Biotechnology

Enzyme Vector Illustration Vectormine Enzymes Biology Biology Lessons Teaching Biology

Enzymes Kinetics And Diagnostic Use Biochemistry Enzyme Kinetics Enzymes

Biology Flow Chart For Cellular Respiration Complete Respiration Flow Chart Cellular Respiration From Gly Teaching Biology Biology Classroom Science Biology

Pin On Enzymes Catalysis Regulation

What Is Enzyme In Biology Structure Location And Function Biology Enzymes Life Science

Image Result For Dna Replication And Enzymes Biologia

Enzyme Classes Molecules Biochemistry Bond

Lock And Key Model Vs Induced Fit Model Fitness Models Lock And Key Biochemical
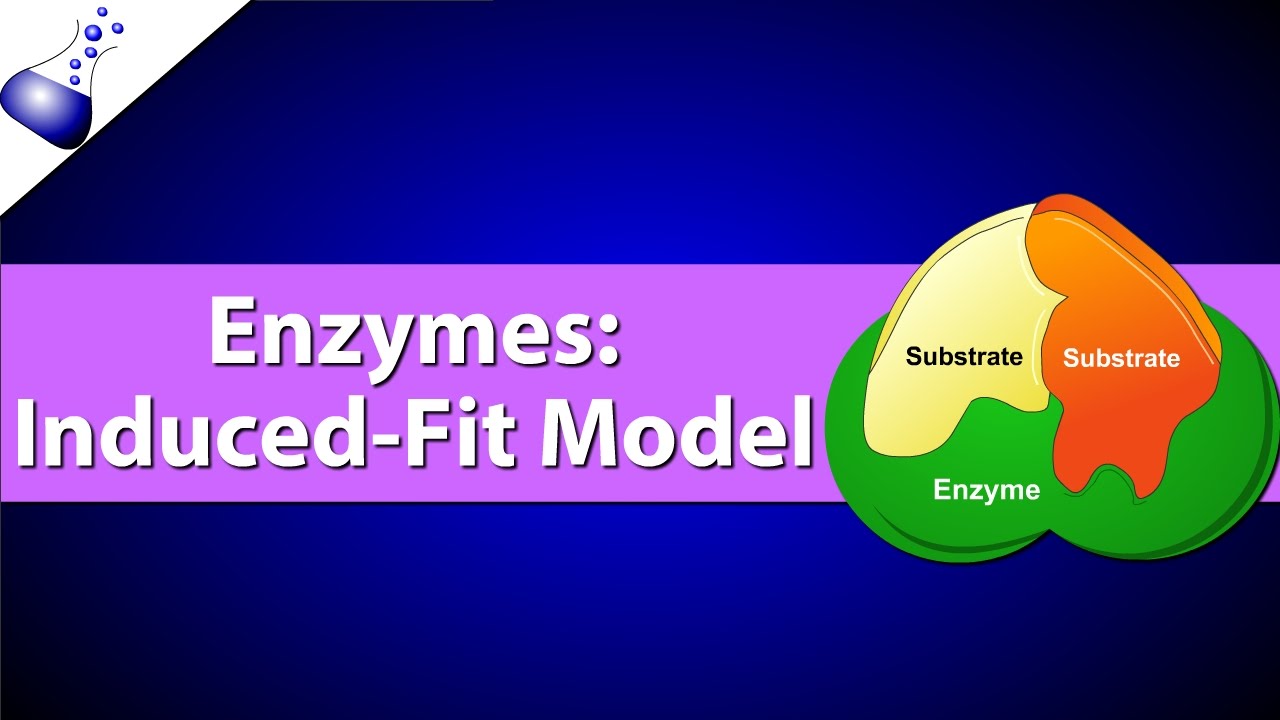
Enzymes The Induced Fit Model Youtube Enzymes Fitness Models Biochemistry

Comments
Post a Comment